Epidemiological research is needed to address the gaps that hamper effective TB control and to contribute to better understanding of the epidemiology of TB. It is important to understand the causes and distribution of TB in populations and identification of the areas for targeted intervention. The current approaches and tools are inadequate to achieve a rate of decline of TB incidence by 17% per year to progress to elimination of TB. The reasons may be attributable to persistent transmission due to a variety of host, pathogen and environmental factors. The actual burden of TB should be quantified in various populations and high-risk groups in endemic settings, and variations in the dynamics of TB in these populations and high-risk groups should be investigated.
The goal of this domain would be to improve knowledge of the distribution and natural history of TB, various determinants to improve cure rates, impact policy-making and ensure more efficient methods of service delivery- epidemiological research.Evidence from implementation/ operational research is critical to help ensure that the most vulnerable have access to critical TB health services.
It would facilitate greater collaboration with other scientific disciplines to understanding the epidemiological aspects, the nature and contribution of specific risk factors and to define the best courses for intervention. It would ensure a sustained, adequate investment in fundamental science as this is essential to maintain the flow of new technologies into the product pipeline, and that new candidate products and strategies enter clinical development. It would provide an interactive and common platform for researchers in all the biomedical disciplines, including basic research, translational research, product development science, clinical research and epidemiology, in order to make significant, timely advances in the control of TB.

This component shall thus lead from quantification of the burden of disease and its determinants at population level, to assessment of the effect of TB control interventions and identification of social and health system factors to improve these interventions and to translate the findings of research into routine programme.

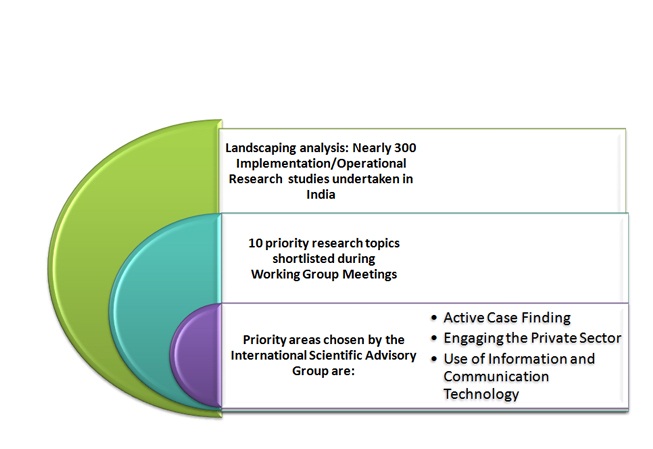
A landscape analysis of more than 300 Implementation/ Operational Research studies in Indiahas revealed manysuccessful interventions for filling the gaps to augment the Programme performance. The most important areas to be undertaken on priority are:
Click here to view the Implementation Research Portfolio
ITRC: India TB Research Consortium