For a low resource setting like India, there is a dire need to have affordable, portable and rapid tests for TB diagnosis. Sputum smear microscopy, a conventional method for detecting Mycobacterium tuberculosis (M.tb), is more than 100 years old. Culturing M.tb takes about 3-6 weeks to yield results. For drug susceptibility tests, this may take even longer. This leads to a prolonged delay in diagnosis, ultimately resulting in delayed treatment which could exacerbate the course of the disease. The global introduction of a diagnostic Nucleic Acid Amplification Test (NAAT),has brought about a revolution in TB diagnosis as it not only rapidly detects TB but also resistance to rifampicin.
The goal of this domain would be to develop and ensure access to new and improved diagnostics to detect active disease at the point of care, diagnose latent TB infection, predict disease progression, and rapidly screen drug resistant TB and paediatric TB.
ITRC will accelerate the development of an indigenous point of care accurate diagnostics suitable to Indian conditions. This could help improve access to rapid and early diagnosis of TB and save millions of dollars in foreign exchange as all modern diagnostic tests for TB are currently imported. ITRC could also help validate and approve the entry of TB diagnostics controlling the use of sub-optimal diagnostics, thus ensuring that patients receive effective and accurate diagnostic technologies.
ITRC will accelerate the development of an Indian point of care accurate diagnostics suitable to Indian conditions. This could help improve access to rapid and early diagnosis of TB and save millions of dollars in foreign exchange as all modern diagnostic tests for TB are currently imported. ITRC could also help validate and approve the entry of TB diagnostics controlling the use of sub-optimal diagnostics, thus ensuring that patients receive effective and accurate diagnostic technologies.


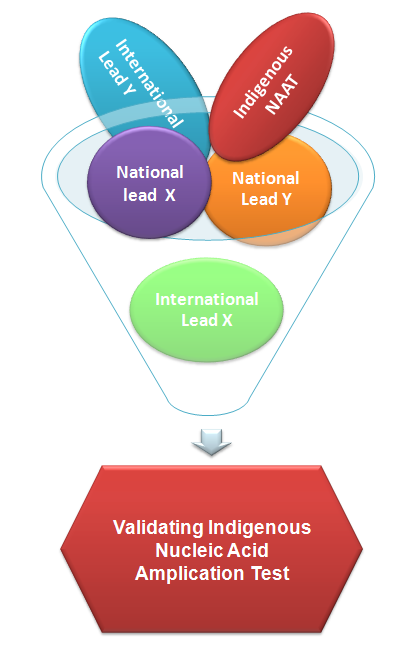
A detailed report of the current status of national and international leads in diagnostics has been developed. Through a series of intensive discussions with experts and other stakeholders, an indigenous Nucleic Acid Amplification Test (NAAT) has been identified for validation and testing. This test is highly sensitive and specific for detecting TB and provides results within an hour compared to the conventional methods that can take days to report results. The test can be used at DMC level and can replace smear in future. In terms of cost effectiveness, the indigenous test can bring about a revolution in transforming the diagnostics landscape for not only India, but also for low and middle income countries.
Click here to view the Diagnostics Research Portfolio
ITRC: India TB Research Consortium