Page 76 - Htain Manual
P. 76
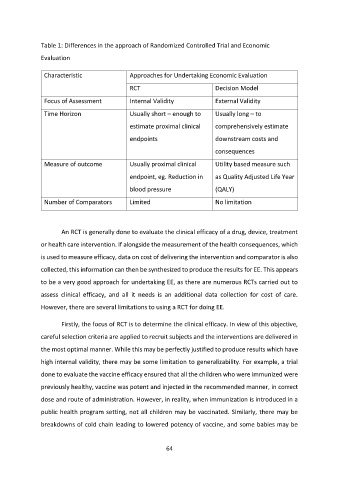
Table 1: Differences in the approach of Randomized Controlled Trial and Economic
Evaluation
Characteristic Approaches for Undertaking Economic Evaluation
RCT Decision Model
Focus of Assessment Internal Validity External Validity
Time Horizon Usually short – enough to Usually long – to
estimate proximal clinical comprehensively estimate
endpoints downstream costs and
consequences
Measure of outcome Usually proximal clinical Utility based measure such
endpoint, eg. Reduction in as Quality Adjusted Life Year
blood pressure (QALY)
Number of Comparators Limited No limitation
An RCT is generally done to evaluate the clinical efficacy of a drug, device, treatment
or health care intervention. If alongside the measurement of the health consequences, which
is used to measure efficacy, data on cost of delivering the intervention and comparator is also
collected, this information can then be synthesized to produce the results for EE. This appears
to be a very good approach for undertaking EE, as there are numerous RCTs carried out to
assess clinical efficacy, and all it needs is an additional data collection for cost of care.
However, there are several limitations to using a RCT for doing EE.
Firstly, the focus of RCT is to determine the clinical efficacy. In view of this objective,
careful selection criteria are applied to recruit subjects and the interventions are delivered in
the most optimal manner. While this may be perfectly justified to produce results which have
high internal validity, there may be some limitation to generalizability. For example, a trial
done to evaluate the vaccine efficacy ensured that all the children who were immunized were
previously healthy, vaccine was potent and injected in the recommended manner, in correct
dose and route of administration. However, in reality, when immunization is introduced in a
public health program setting, not all children may be vaccinated. Similarly, there may be
breakdowns of cold chain leading to lowered potency of vaccine, and some babies may be
64